HIPAA Compliance with DuploCloud
Secure Your Healthcare Data with DuploCloud DevOps automation platform
Simplify Your HIPAA Compliance Journey with DuploCloud
How Can
DuploCloud Help
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliance is critical for businesses in the healthcare sector dealing with Protected Health Information (PHI). The requirements landscape can be intricate and daunting, but DuploCloud transforms this challenge into an effortless process. Our solution eases HIPAA compliance, ensuring your healthcare data is secure, your processes streamlined, and your business ready to face the demands of the healthcare industry confidently.
Key Features
Automated Compliance Processes
Robust Data Security
Centralized Visibility
Continuous Compliance Checks
Continuous Updates
Automated Encryption and Backup
Resources
DuploCloud's resources section is packed with valuable content to help you learn more about DevOps automation and how to get the most out of our platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
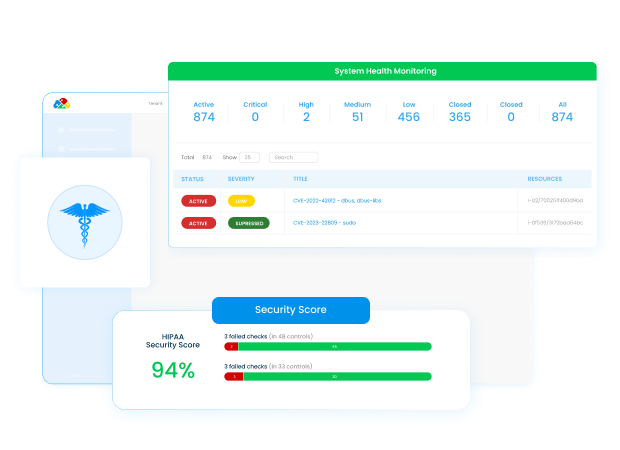
DuploCloud keeps up-to-date with changes in compliance regulations by using a dynamically-updated rules database. This database constantly monitors and updates the environment according to the latest compliance and security standards. Users are notified of any variances in compliance and security standards, which are assigned severity priorities. This allows users to address and update their environment at their convenience.
DuploCloud uses encryption for data at rest and in transit to protect ePHI. It orchestrates KMS keys per tenant for encrypting various AWS resources like RDS DBs, S3, Elastic Search, and REDIS. For data in transit, DuploCloud uses certificates from Cert-Manager to enable TLS encryption, ensuring the protection of ePHI as per HIPAA guidelines.
DuploCloud maintains comprehensive audit trails in addition to AWS CloudTrail, logging all write events about infrastructure changes in an ELK cluster. It also employs the Wazuh agent to track activities at the host level, with CloudTrail, audit, and Wazuh agent events consolidated in the Wazuh dashboard. This fulfills HIPAA's requirements for regular review of information system activities.
DuploCloud’s tenant model implements strict access controls, allowing access based on user roles. This mechanism integrates into the VPN client, ensuring that each user's access is appropriately restricted. By default, no access to a tenant is allowed unless specific ports are exposed via an elastic load balancer, aligning with HIPAA's requirements for safeguarding access to ePHI.
DuploCloud’s infrastructure is designed with multiple availability zones to ensure resilience and continuity in case of emergencies or system failures. This setup allows for the dynamic transfer and resumption of system operations, ensuring the protection and accessibility of ePHI even in emergency modes, as required by HIPAA regulations.




Ready to get started?
Boost DevOps efficiency, accelerate compliance, enhance security, and drive innovation with DuploCloud.